CSS Position 属性
CSS 中,position 属性用于指定元素的定位方式。position 属性有五个值:
staticrelativefixedabsolutesticky
运用这些值,可以实现元素的不同定位方式。
position: static;
position: static; 是元素的默认定位方式。静态定位的元素不受 top、bottom、left 和 right 属性的影响。
静态定位的元素不会以任何特殊方式定位。
position: relative;
position: relative; 是元素相对于其正常位置定位的方式。
设置相对定位元素的 top、right、bottom 和 left 属性会使其相对于正常位置调整。其他内容不会调整以适应元素留下的任何空白。
position: fixed;
position: fixed; 是元素相对于视口定位的方式,这意味着即使页面滚动,元素始终保持在同一位置。top、right、bottom 和 left 属性用于定位元素。
固定定位的元素不会在页面上留下空白。
position: absolute;
position: absolute; 是元素相对于最近的定位祖先定位的方式(而不是相对于视口定位,如固定定位)。
但是,如果绝对定位的元素没有定位祖先,则使用文档主体,并随页面滚动而移动。
注意: 绝对定位的元素是不在正常流中的,而且可以重叠元素。
position: sticky;
position: sticky; 是基于用户滚动位置定位的方式。
粘性元素在相对定位和固定定位之间切换,具体取决于视口中是否满足给定的偏移位置 - 然后它在那里“粘住”(类似 position: fixed)。
一些技巧
重叠元素
当元素被定位时,它们可以重叠其他元素。
z-index 属性指定元素的堆叠顺序(哪个元素应该放在其他元素的前面或后面)。
<style>
.box1 {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
z-index: 1;
}
.box2 {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
z-index: 2;
}
</style>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
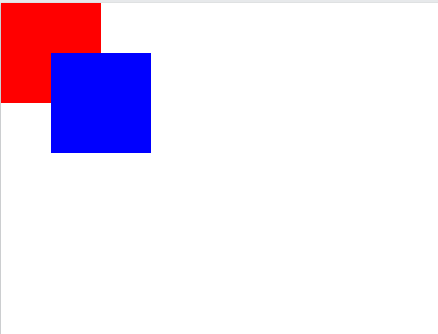
这个例子中,蓝色盒子 .box2 的 z-index 值比红色盒子 .box1 的值大,所以蓝色盒子在红色盒子的上面。当然,他们是用 position: absolute; 定位的。
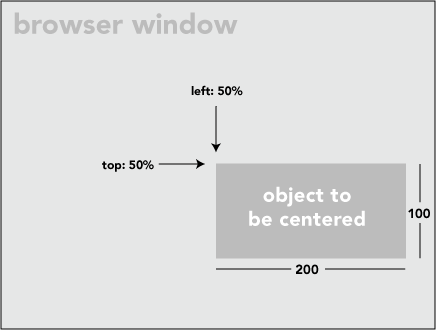
将对象精确居中
.centered {
position: fixed; /* or absolute */
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
}
.centered {
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
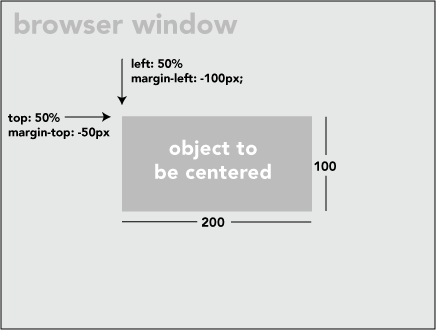
这个例子中,.centered 类用于将元素精确居中。首先,将元素的左上角放在页面的中心,然后使用 transform 属性将元素的中心放在页面的中心。
总结
CSS 中的 position 属性用于指定元素的定位方式。position 属性有五个值:static、relative、fixed、absolute 和 sticky。通过这些值,可以实现元素的不同定位方式,从而实现页面布局的灵活性和多样性。